general
The coordinate systems#
It exists 4 possible coordinate representations but only two are used in genomics:
- 0-based half-open
- 1-based fully closed
Let's dive into the coordinates systems complexity.

Coordinate system | Range | Example | Size of the range | Array indexing in programming | Institute/DB/ File Format | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - 0-based, fully closed - 0-base inclusive start, inclusive end - [0,] | [start, end] | [1,3] = TGC | end - start + 1 | |||
| - 0-based, half-open - 0-base inclusive start, exclusive end - [0,) | [start, end) | [1,4) = TGC | end - start | Bash, C, C++, ksh, Go, Haskell, Java, JS, Perl, Python, PowerShell, Ruby, Rust, Scala | UCSC DB, Genebank DB, BED, BAM, BCFv2, PSL, ASN, BigBed, bedGraph, GA4GH; HML 1.0 | |
| - 1-based, fully closed - 1-base inclusive start, inclusive end - [1,] | [start, end] | [2,4] = TGC | end - start + 1 | AWK, COBOL, Fortran, Julia, Lua, MATLAB, R, sh, XPath/Xquery, zsh | Ensembl, UCSC genome browser, Genbank file, GFF, GTF, SAM, VCF, Wiggle, GenomicRanges, BLAST, GenBank/EMBL Feature Table, HGVS | /!\ when describing indel you must know if the insertion is before or after the position |
| - 1-based, half-open - 1-base inclusive start, exclusive end - [1,) | [start, end) | [2,5) = TGC | end - start |
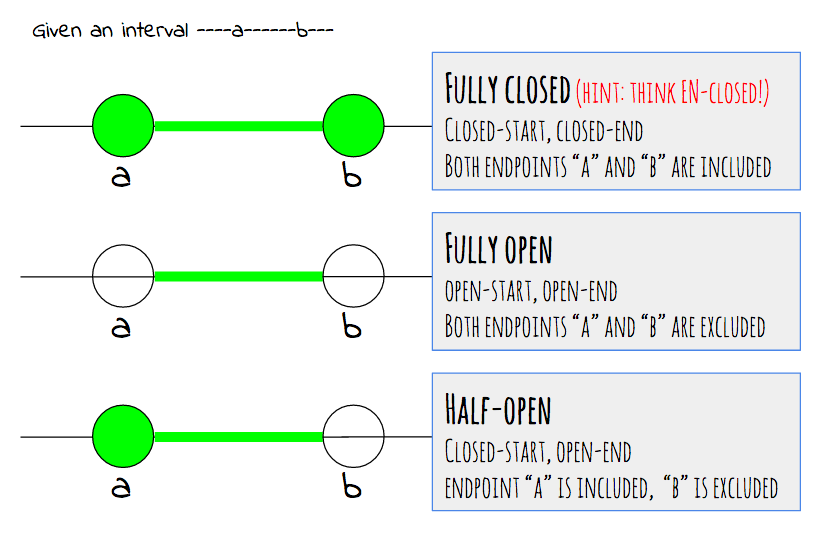
Interval types#
I like this visual explaining the interval types. Credits is from UCSC Genome Browser Blog